(EXPERIMENTAL) Drawing SVG paths¶
Using the drawSVG function¶
To import the drawSVG function:
from turtlethread.draw_svg import drawSVG
This function takes in 3 compulsory positional arguments: a turtle, the svg file path string, and the height of the SVG. The width can also be passed as a 4th positional argument, and defaults to the same value as the height.
The keyword arguments it takes are:
fill: bool, optional. If True, the SVG will be filled. Default is True.outline: bool, optional. If True, the SVG will be outlined. Default is False.full_fill: bool, optional. If True, the SVG will be fully filled if set to fill, otherwise it will be partially filled. Default is True.fill_min_y_dist: int, optional. The minimum distance between fill points in the y direction. Default is 10 (1mm).fill_min_x_dist: int, optional. The minimum distance between fill points in the x direction. Default is 10 (1mm).
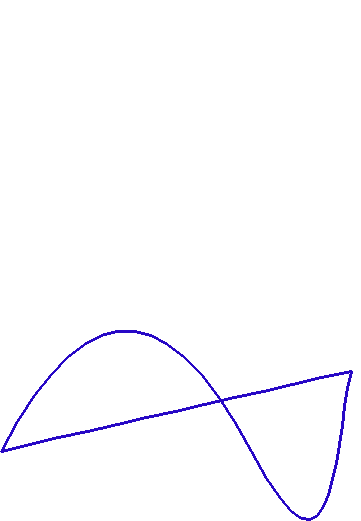
Here is a sample of it in action:
1import turtlethread
2te = turtlethread.Turtle()
3from turtlethread.draw_svg import drawSVG
4drawSVG(te, "svg_with_c.svg", 250, 400, fill=False, outline=True)
Debugging the SVG file¶
If you encounter issues with your SVG file, try the following checklist:
If it is fill: check that the fill path does not cross itself - Our fill algorithm may not work if the path of the SVG crosses over - Our fill feature is also very experimental, and there is a high chance of it having errors as of now.
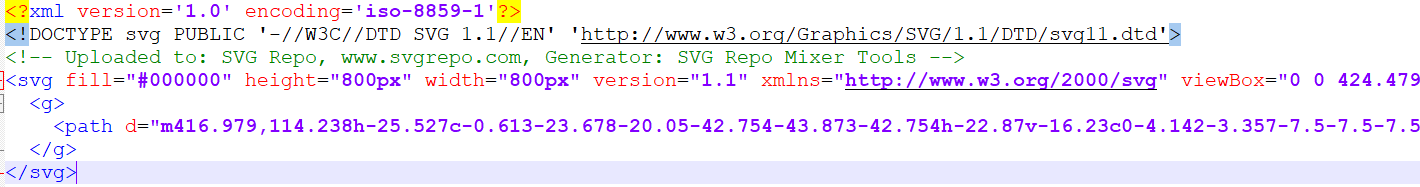
Viewing the SVG file as text¶
To view an SVG file as text, open an SVG file with a basic text editor like Notepad/Notepad++, or draw an SVG file into it. This will show the text of the SVG file, which should look like the below image:
viewBox attribute¶
In the <svg> tag in the SVG file, there should be a viewBox attribute, such as the following tag:
<svg fill="#000000" height="800px" width="800px" version="1.1" viewBox="0 0 424.479 424.479" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
If the viewBox attribute does not exist, you should create it yourself; this defines the 0% and 100% positions that the later SVG commands will use. Normally, if an SVG file does not specify the viewBox, you can use its height and width. For example:
<svg width="400" height="250" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
Can be changed to
<svg width="400" height="250" viewBox="0 0 400 250" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
We have not tested on SVG files with their viewBox starting with anything but 0 0, so there might be issues with those SVG files. For those, please raise a GitHub Issue for us to resolve it.
<path> tag¶
In our program, we only draw the paths enclosed in a <path> tag in the SVG file. For example, we can see in the screenshot of what an SVG file looks like that there is a <path> tag that contains a string describing the path that the SVG file takes. First, check that the SVG path you are trying to draw is in a <path> tag. Ensure that the path string ends with a “z” or “Z”, which signals the end of the path. If it does not have one, then add it.
If nothing works¶
Raise a GitHub Issue.